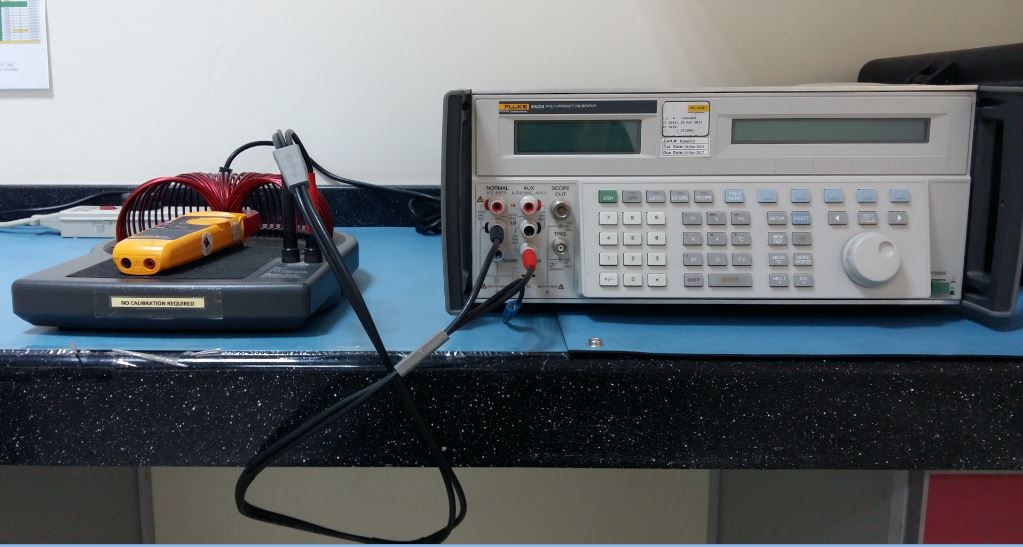
Humidity Calibration has been an important part of scientific study since the beginning of time, but the process has just recently become accessible to the average person with the introduction of accurate humidity sensors that can be easily calibrated.
If you have one of these sensors and are not aware of the importance of keeping it calibrated or how to calibrate it properly, this article is for you! In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about humidity calibration, including why you need to calibrate your humidity sensor and how to go about doing it. Let’s get started!
What is humidity calibration?
Humidity is an important measurement in space. It tells you how much water vapour is in the air and can be used as an indicator of comfort, general building health, and indoor air quality.
The humidity measurement reported by our monitor will only be accurate if we calibrate it with a known source of accurate relative humidity. How do we calibrate it? The key is temperature; the rule of thumb is that the higher the temperature, the higher our humidity sensor should read for calibration purposes.
Why is it important to measure humidity?
Humidity is a vital factor in maintaining a comfortable temperature inside your home. If the humidity level is too high, it leads to problems such as mould growth and the accumulation of dust.
On the other hand, if humidity is too low, it can lead to condensation on windows, which then leads to mould growth.
It also causes people to feel colder because they are not able to sweat when the air is dry. To make sure that you have an accurate reading of how humid your indoor environment is, you need to calibrate your sensor once every month or so with a standard hygrometer.
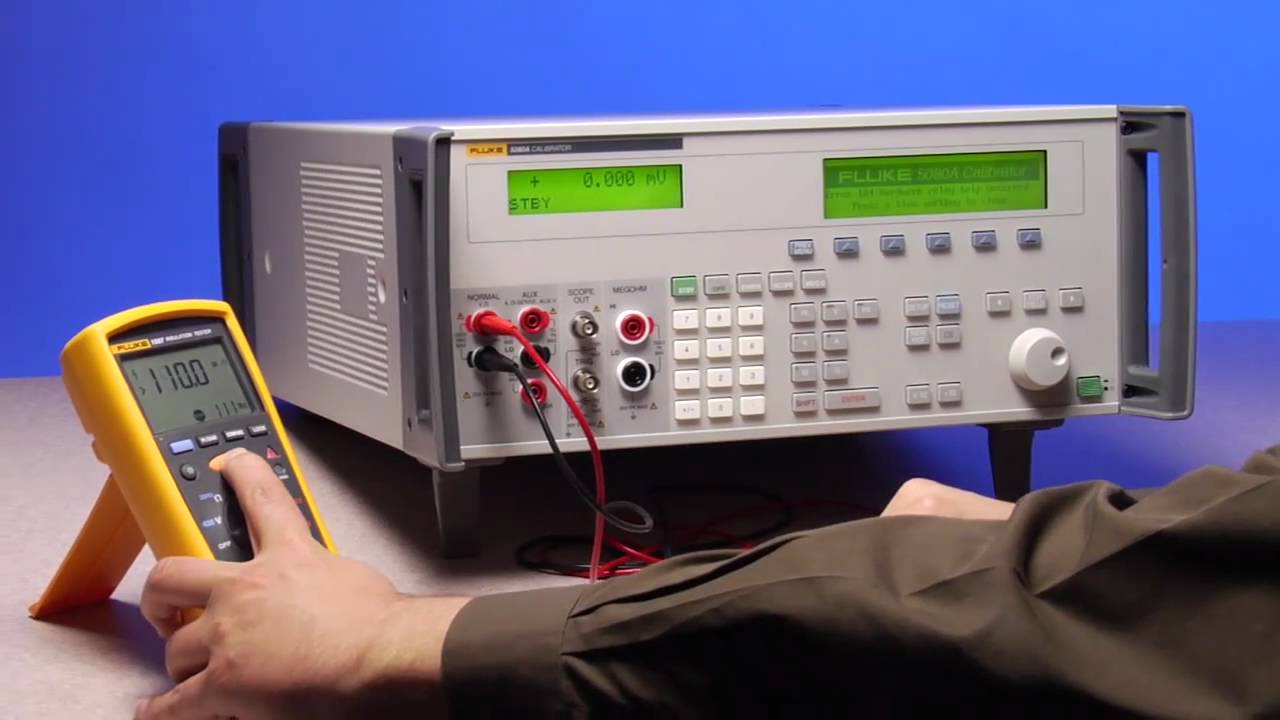

What types of instruments measure humidity?
There are many instruments that can measure humidity, such as a hygrometer, psychrometer, capacitance sensor, and infrared temperature-humidity-pressure (THP) sensor.
A common device for measuring relative humidity is the mechanical psychrometer. These devices rely on wet-bulb depression or dry-bulb thermometer measurements to determine the air’s relative humidity.
This method compares the temperature at which a water droplet evaporates with the dew point temperature of an air sample in order to obtain relative humidity information. There are many products available, like wireless sensor networks and energy-saving control systems that can measure indoor humidity levels and monitor outdoor climate changes.
How to calibrate your temperature and humidity sensor
The data you are collecting is not accurate if your sensor isn’t calibrated. Here’s how to do it: Take a pot or bowl and fill it with hot water and two cups of ice cubes (make sure the pot has enough room for the sensor).
Place the probe of your temperature/humidity meter into the water, preferably as close as possible to the ice cubes. Set it on your desired measurement setting, wait 10 minutes, and read off the measurement results.
Tips to ensure a successful humidity measurement
Invest in a standalone humidity sensor to keep tabs on your environmental conditions, whether it be the air indoors or outside. Store the device and its accessories somewhere safe from moisture and corrosive vapours.
Readings are usually most accurate when taken within an hour of initialization, so check with your device’s user manual for how long it takes before readings become stale.